Advantages and Disadvantages of PTFE O-Rings: A Complete Guide
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) O-rings are a trusted sealing solution in industries where extreme conditions demand more than standard elastomers can handle.
From aerospace and automotive to chemical processing and medical devices, PTFE O-rings offer unique advantages that make them indispensable — but they also come with trade-offs that engineers must carefully consider.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about PTFE O-rings: their strengths, limitations, best applications, and how to choose the right seal for your needs.
What Are PTFE O-Rings? An Inside Look at Fluoropolymer Seals
PTFE is a synthetic fluoropolymer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, wide operating temperature range, and low friction properties. These characteristics make PTFE O-rings an ideal choice for demanding sealing applications where traditional rubber compounds fail.
Unlike elastomer O-rings, which can degrade under harsh chemicals or elevated heat, PTFE O-rings maintain integrity and performance in extreme environments. However, PTFE’s rigidity and limited elasticity also mean that it behaves differently in a seal groove, requiring careful design and installation considerations.
PTFE Grades and Fillers: Tailoring Performance for Specific Needs
Not all PTFE O-rings are created equal. While virgin PTFE provides outstanding chemical resistance and purity, filled PTFE grades offer improved mechanical properties that address some of PTFE’s weaknesses. By adding reinforcing materials to the polymer, manufacturers can optimize O-rings for specialized conditions:
- Glass-filled PTFE: Improves dimensional stability and reduces cold flow, making it a strong choice for high-pressure static applications.
- Carbon-filled PTFE: Enhances wear resistance and compressive strength, useful in dynamic sealing environments.
- Graphite-filled PTFE: Provides better thermal conductivity while retaining PTFE’s chemical inertness.
- Bronze-filled PTFE: Offers higher strength and reduced creep, though with slightly lower chemical resistance.
Choosing the right PTFE blend allows engineers to fine-tune performance for their exact application, ensuring the O-ring is not just durable but also efficient in its operating environment.
Unmatched Advantages of PTFE O-Rings
PTFE O-rings provide numerous benefits that make them the go-to choice for engineers and manufacturers:
- Chemical Resistance – PTFE resists nearly all aggressive chemicals, solvents, and acids, making it suitable for highly corrosive environments.
- Wide Temperature Range – Performs reliably from cryogenic conditions up to approximately 500°F (260°C).
- Low Friction and Non-Stick Properties – PTFE’s smooth surface minimizes wear and reduces energy loss in dynamic applications.
- Non-Contaminating and Inert – Ideal for food, pharmaceutical, and medical manufacturing where purity is critical.
- Exceptional Shelf Life – Unlike elastomers, PTFE does not degrade or age, ensuring long-term reliability in storage and use.
PTFE O-rings shine where chemical exposure, high temperatures, and durability are non-negotiable.
Performance Trade-Offs: Disadvantages You Should Know
While PTFE O-rings deliver unmatched benefits, they also have limitations:
- Lack of Elasticity – PTFE does not compress or stretch like elastomers, which can make sealing more difficult in certain applications.
- Cold Flow / Creep – Under sustained pressure, PTFE can deform permanently, leading to leakage over time.
- Installation Challenges – PTFE’s rigidity makes it prone to cracking or distortion if improperly installed.
- Poor Low-Pressure Sealing – Without elasticity, PTFE O-rings may not seal effectively in low-pressure static applications.
Understanding PTFE’s weaknesses is critical to designing grooves, selecting backup rings, and ensuring proper installation.
Cost Considerations: PTFE vs Elastomers and Hybrids
Beyond performance, cost plays a significant role in seal selection. PTFE O-rings generally cost more than traditional elastomers like NBR, EPDM, or Viton®, both because of the raw material and the machining required for production.
However, the initial price tells only part of the story. PTFE’s longer service life, resistance to chemical attack, and ability to operate in extreme environments often reduce overall lifecycle costs.
For industries where downtime or seal failure is extremely costly — such as aerospace, semiconductor, or pharmaceutical manufacturing — PTFE can deliver a better return on investment despite higher upfront expenses.
In contrast, elastomers remain the most economical choice for standard operating environments, especially when flexibility and resilience are more critical than chemical or temperature resistance.
Best Uses for PTFE O-Rings vs Elastomers
When should you choose PTFE over traditional elastomer O-rings like NBR, EPDM, or Viton®?
Choose PTFE O-Rings When:
- Your system operates in extreme chemical environments.
- High operating temperatures exceed elastomer limits.
- Friction reduction is critical for performance.
- Long-term storage and shelf stability are required.
Stick with Elastomers When:
- You need flexibility and resilience in the seal.
- Applications involve frequent dynamic movement at low pressures.
- Cost efficiency is more important than chemical resistance.
PTFE and elastomer O-rings each excel in different areas. Choosing the right material depends on your application priorities.
Industry-Specific Applications and Case Examples
PTFE O-rings aren’t just versatile — they solve industry-specific problems where elastomers fall short:
- Aerospace: Fuel systems, hydraulic controls, and engine components rely on PTFE to withstand aggressive fuels and wide thermal cycles.
- Automotive: PTFE O-rings in transmissions and emission systems prevent seal degradation from high heat and chemical exposure.
- Medical & Pharmaceutical: Non-reactive and FDA-compliant PTFE ensures sterility in pumps, valves, and drug delivery systems.
- Food & Beverage: PTFE’s non-stick properties prevent flavor carryover and contamination while meeting safety standards.
- Chemical Processing: Strong resistance to acids, solvents, and reactive gases ensures uptime in critical manufacturing equipment.
By tailoring PTFE O-ring solutions to each industry’s unique needs, engineers can maximize performance, safety, and reliability.
When to Choose PTFE O-Rings vs Spring-Energized Seals
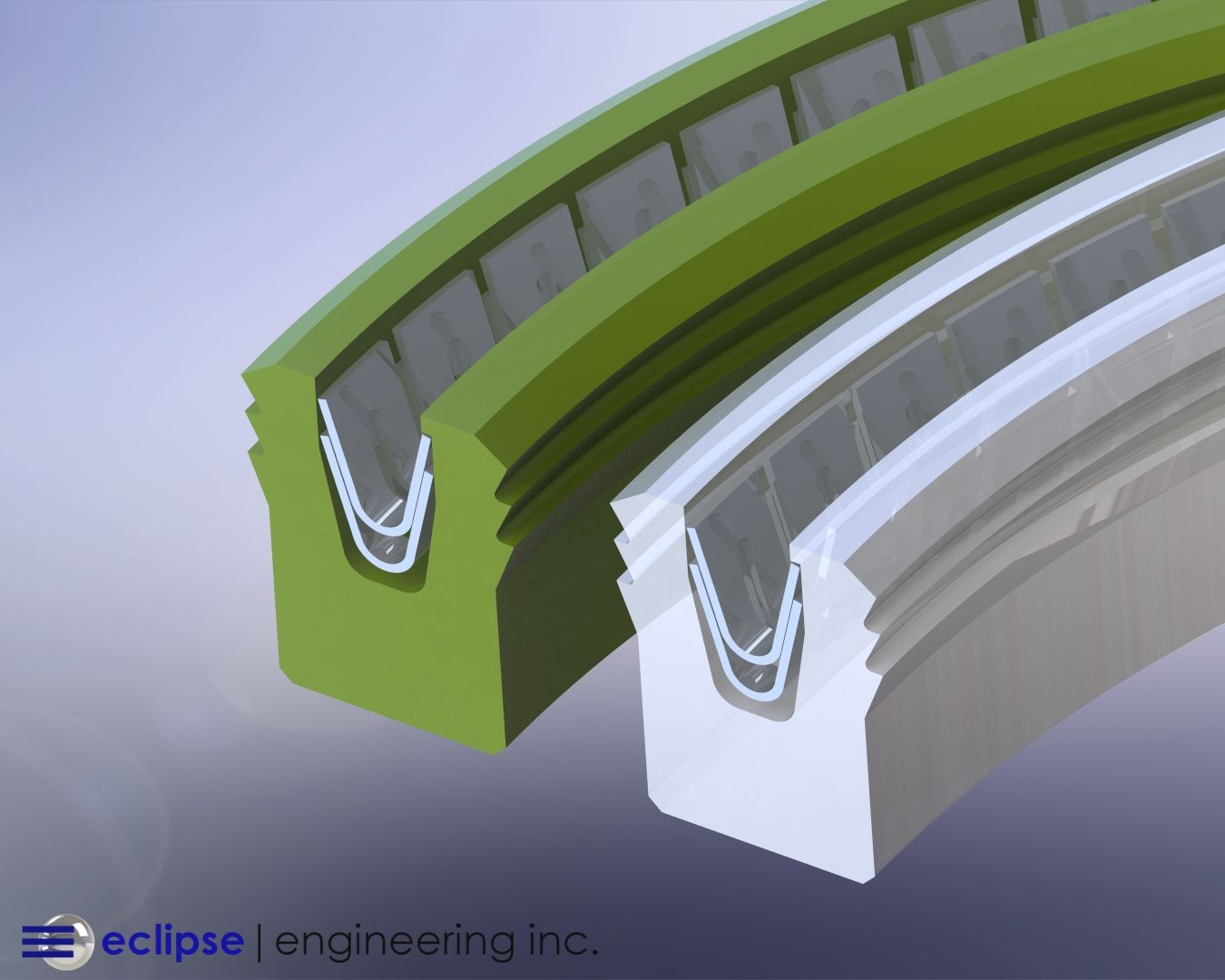
Spring-energized seals are an alternative when PTFE alone cannot provide adequate sealing. These seals combine a PTFE jacket with a metallic spring, which provides the elasticity PTFE lacks.
Advantages of Spring-Energized Seals:
- Maintain sealing force even under low pressures.
- Handle extreme dynamic applications better than plain PTFE O-rings.
- Resist creep deformation thanks to spring support.
When to Use Spring-Energized Seals Instead of PTFE O-Rings:
- In cryogenic applications where contraction reduces sealing force.
- For vacuum applications requiring reliable leak-tight sealing.
- When system pressure cycles frequently.
If your application demands both PTFE’s durability and elastomer-like sealing force, spring-energized seals may be the better fit.
Proper Installation & Long-Term Care of PTFE O-Rings
To get the most from PTFE O-rings, careful installation and maintenance practices are essential:
- Groove Design – Ensure the groove is designed to account for PTFE’s lack of elasticity and cold flow.
- Lubrication – Use compatible lubricants to reduce installation friction and risk of cracking.
- Backup Rings – Employ backup rings in high-pressure applications to prevent extrusion and creep.
- Inspection & Replacement – Regularly inspect seals for deformation, creep, or damage and replace as needed.
Proper installation extends service life and helps PTFE O-rings perform reliably in challenging conditions.
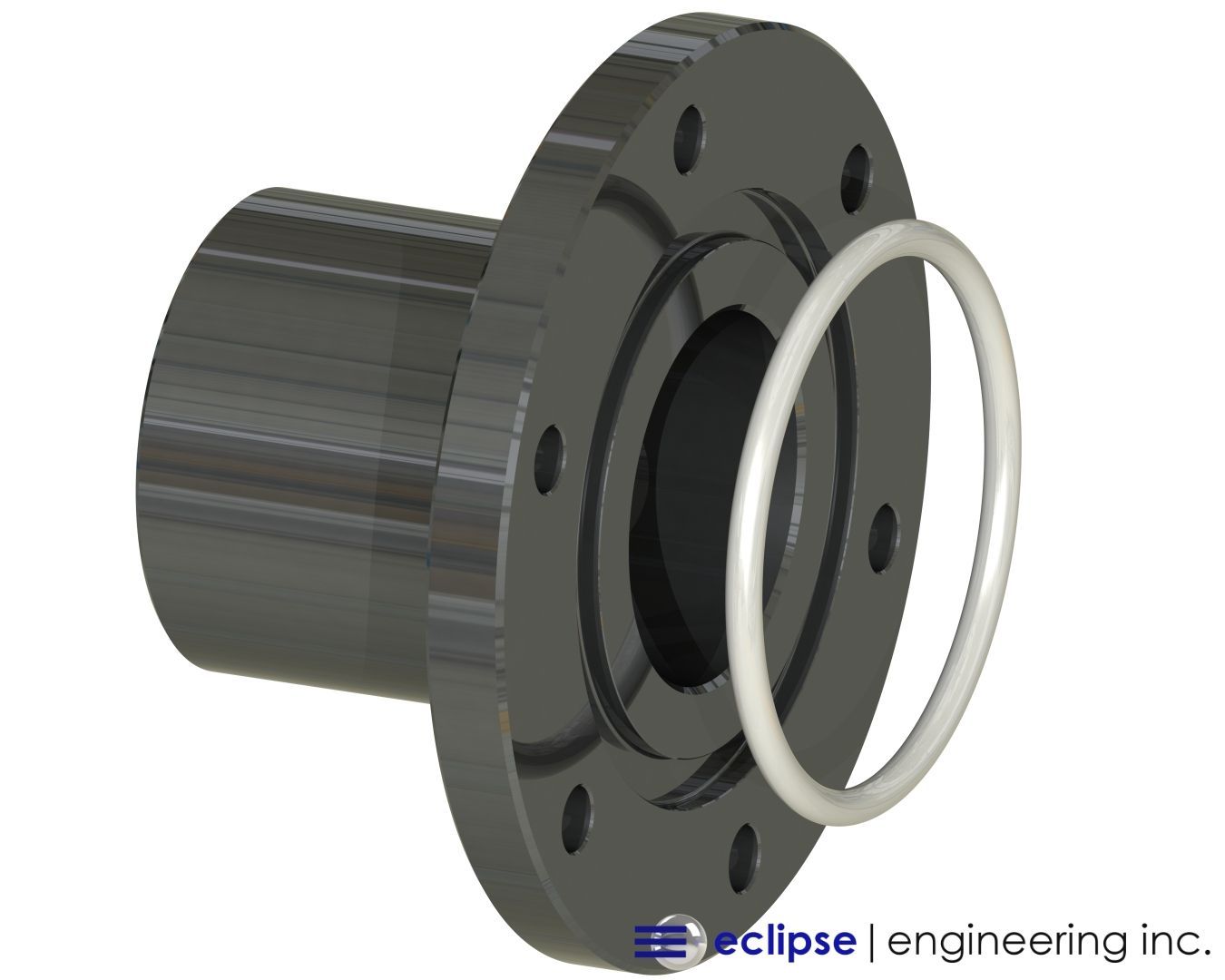

Custom PTFE O-Ring Solutions from Eclipse Seal
Not every sealing challenge can be solved with an off-the-shelf solution. That’s why Eclipse Seal specializes in custom PTFE sealing products designed to meet exact performance requirements.
Our capabilities include:
- Custom-compounded PTFE blends for unique environments.
- FDA, USP Class VI, and other regulatory-compliant materials.
- Engineering support for groove design and material selection.
- Prototype-to-production manufacturing for specialized industries.
Eclipse Seal’s expertise ensures you get a PTFE O-ring tailored to your exact application needs.
How Eclipse Seal Supports Your PTFE Sealing Needs
PTFE O-rings offer unbeatable resistance to chemicals, heat, and wear, making them a powerful sealing option in many industries. However, their limitations in elasticity, creep resistance, and installation complexity mean they are not always the right choice for every application.
The key is understanding when PTFE is the best fit — and when alternatives like elastomers or spring-energized seals may deliver better results.
At Eclipse Seal, we help engineers and manufacturers navigate these choices by providing both off-the-shelf and custom PTFE sealing solutions. Our expertise ensures that your seals perform reliably under the toughest conditions.
Ready to find the right PTFE O-ring solution for your application?
Contact Eclipse Seal today and let our team guide you to the best sealing technology for your needs.