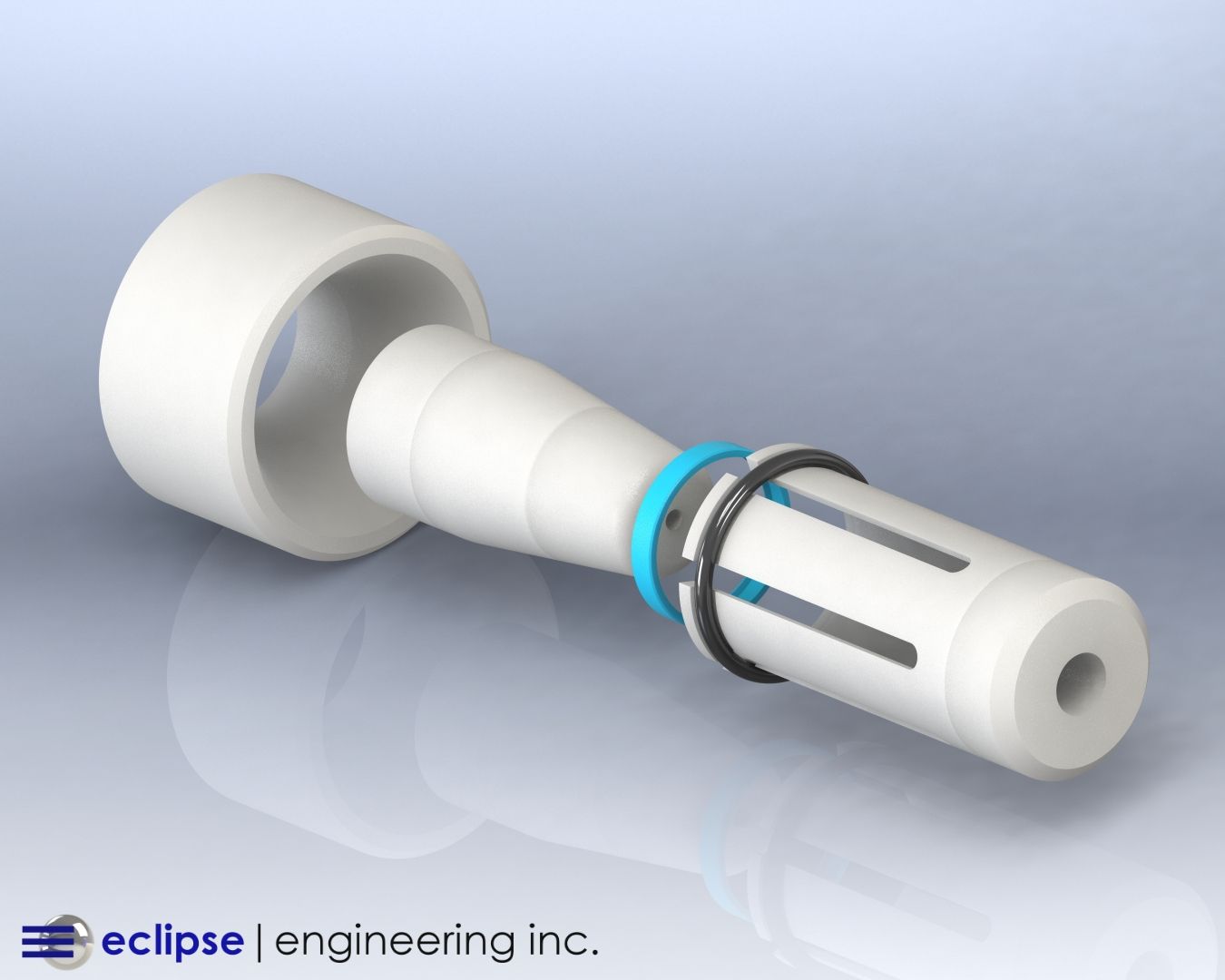
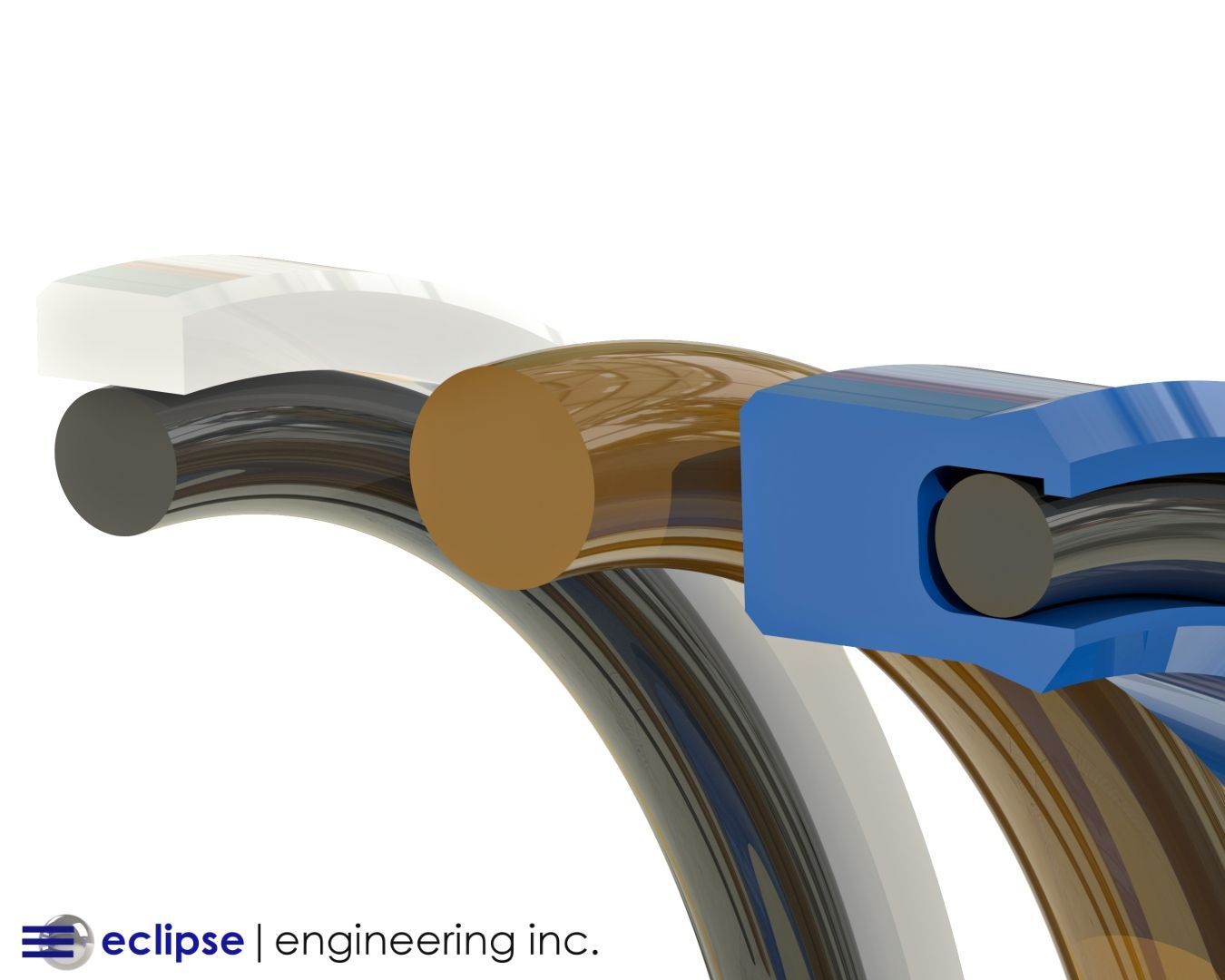
The Pros and Cons of Using UHMW for Your Sealing Application
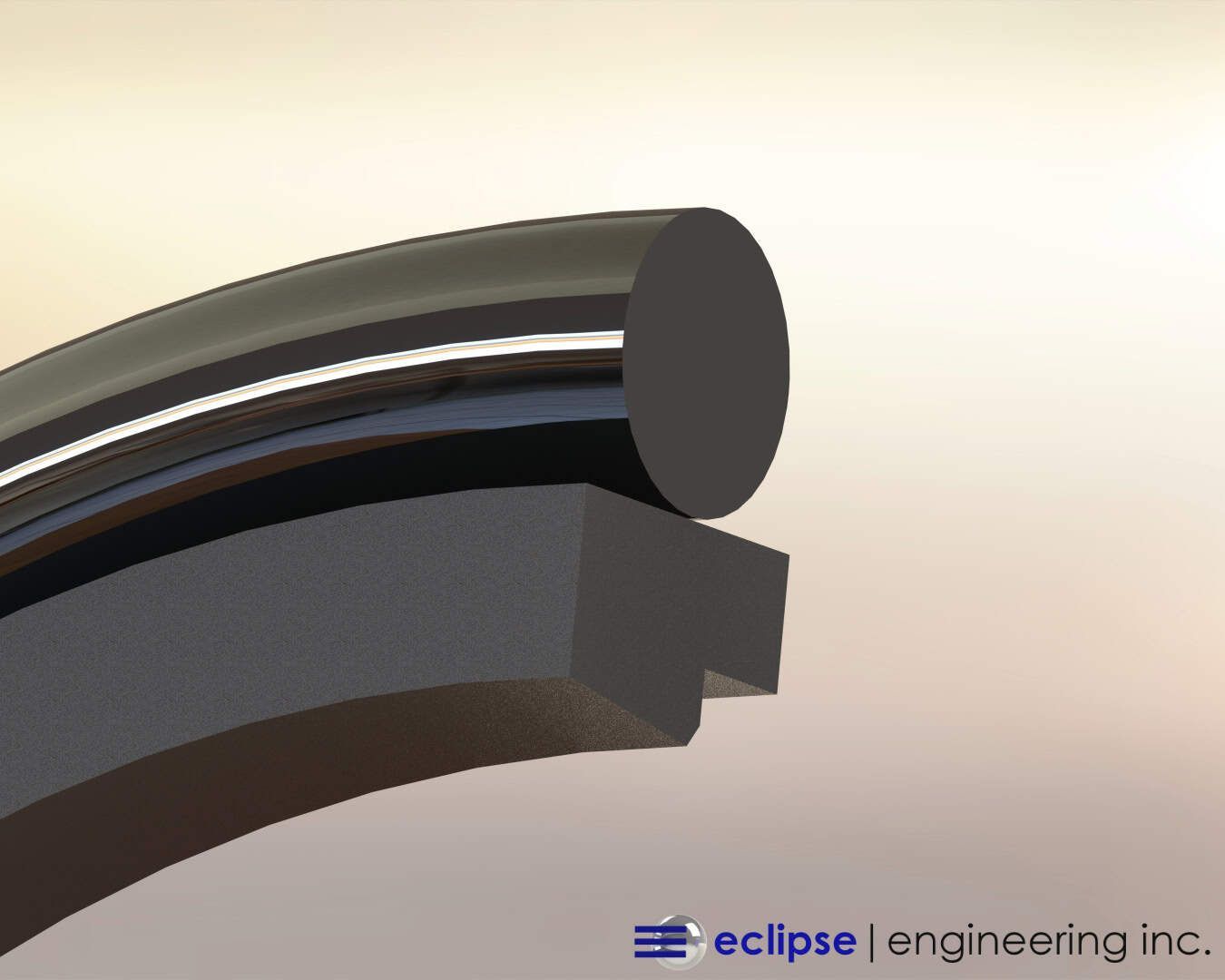
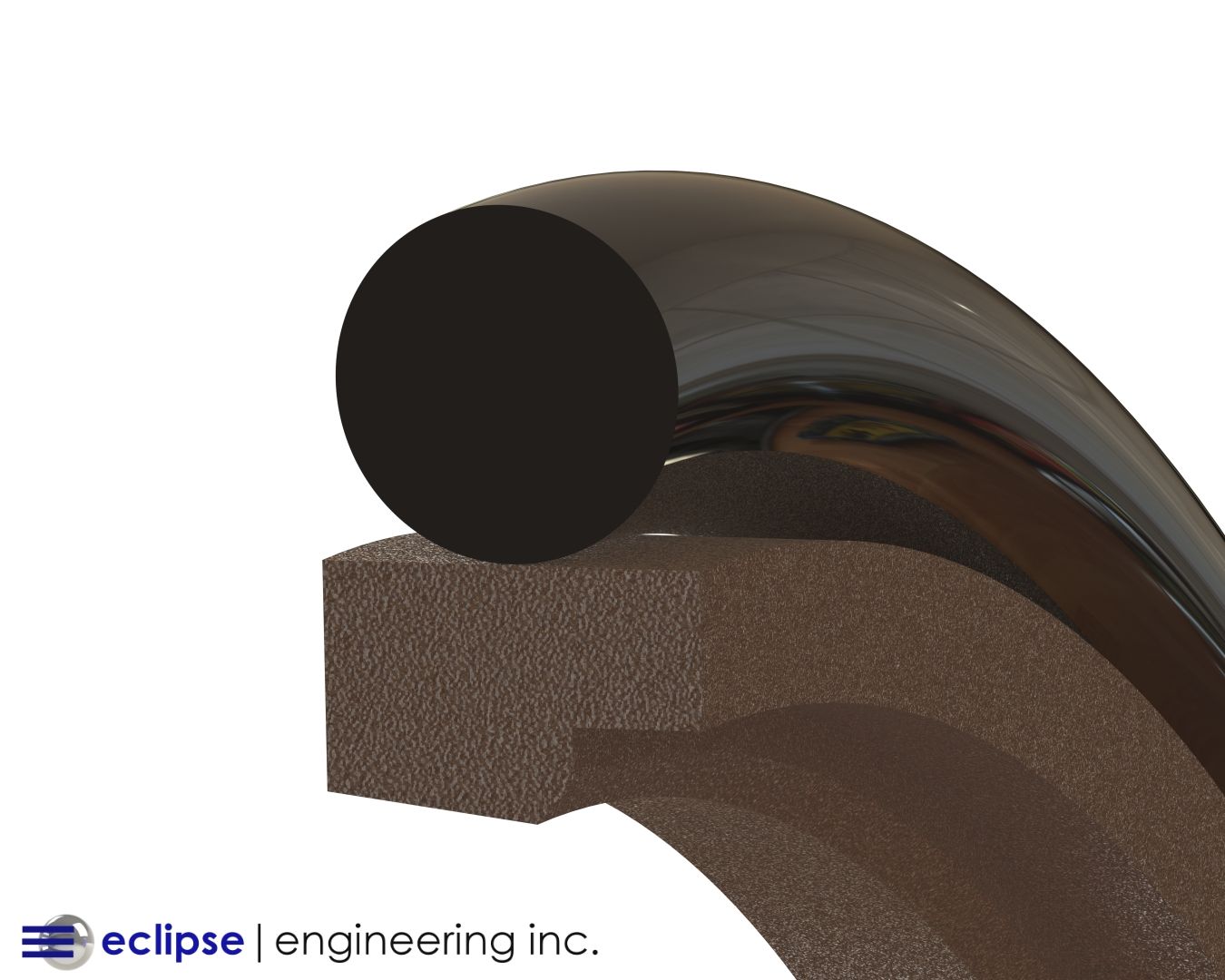
Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMW) continues to be one of the most widely used polymer materials in industrial sealing — especially where wear, abrasion, or tough media conditions are present.
While PTFE and PTFE blends remain the flagship choices for many high-performance seals, UHMW offers a unique combination of durability, low friction, and cost-effectiveness that makes it a compelling option for engineers, designers, and procurement teams.
As a polymer with extremely long molecular chains, UHMW behaves differently from standard polyethylene grades (LDPE or HDPE). Its enhanced toughness, impact resistance, and chemical stability have made it indispensable in applications ranging from abrasive media seals to scraper seals, wear rings, and guide bearings.
Below, we expand on the advantages and drawbacks of UHMW as a sealing material — while offering engineering insight, design considerations, and real-world guidance to help determine whether UHMW is the right choice for your application.
The Advantages of UHMW
UHMW provides a combination of properties that make it ideal for sealing, guiding, and wear applications in demanding environments. It is especially effective when media is abrasive, contaminated, or chemically complex.
Exceptional wear, abrasion, tear, and cut resistance
UHMW’s durability is foundational to its appeal. Its long molecular chains give it exceptional toughness—significantly greater than many PTFE blends. In extremely abrasive environments, UHMW’s wear life can exceed PTFE by 10× or more.
This makes UHMW a smart choice in slurry pumping, ceramic-filled coatings, and mineral-processing equipment, where the media behaves like “liquid sandpaper.”
Its toughness also contributes to UHMW’s ability to handle abrasive and particulate-laden media without compromising performance.
Superior performance in abrasive and particulate-laden media
When dealing with abrasive or particulate-filled media, UHMW’s toughness enables it to maintain sealing integrity and prolong system uptime.
Alongside abrasion resistance, UHMW provides effective scraping and wiping capabilities that make it ideal for heavy-duty seal applications.
Effective scraping and wiping capability
UHMW maintains a sharp, point-loaded leading edge, making it ideal for scraper seals that must prevent buildup from sticky, gummy, or viscous media such as epoxies, resins, or slurries.
Combined with its low-friction properties, UHMW reduces heat and wear in dynamic applications, further extending seal life.
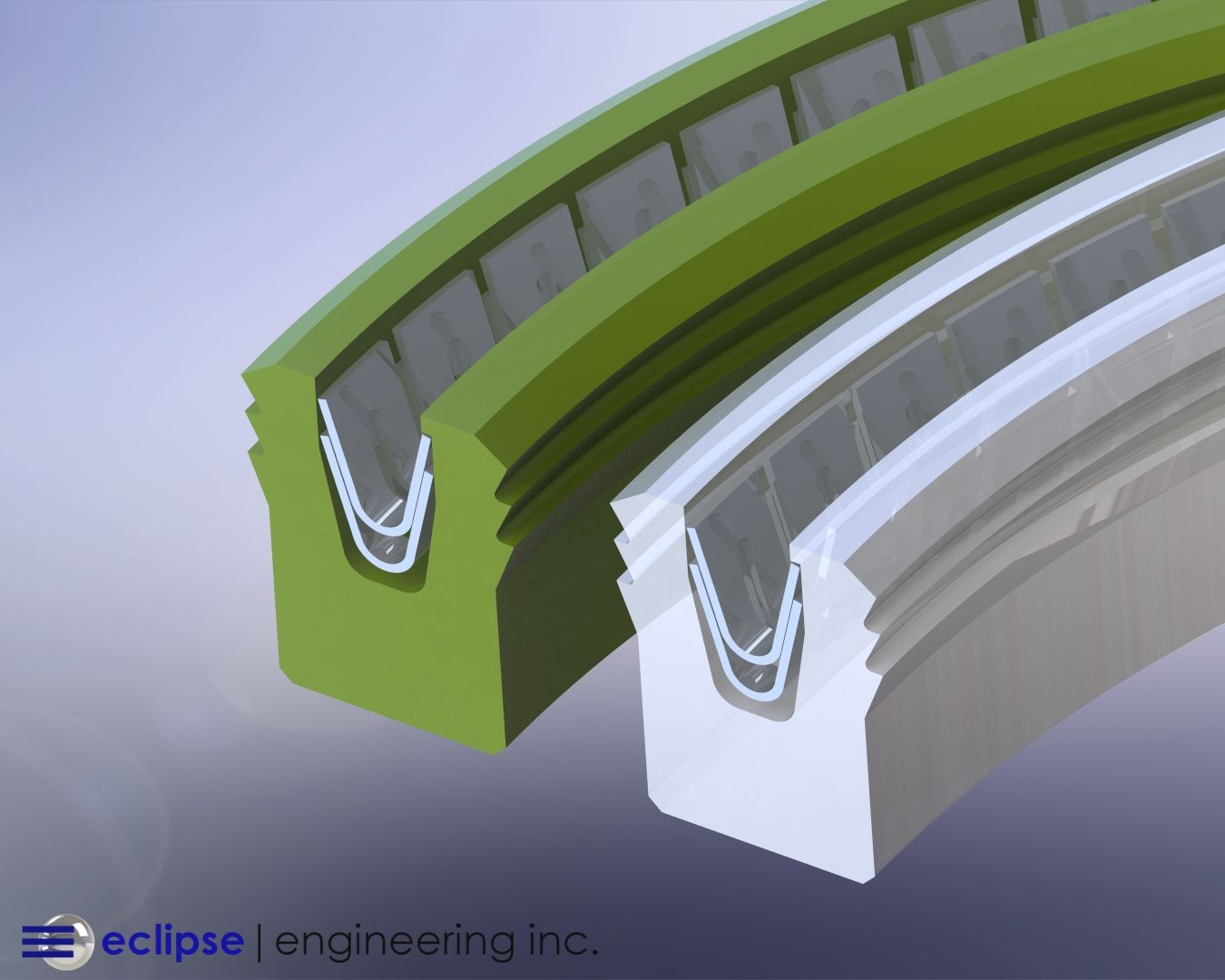
Low coefficient of friction
While not as low as PTFE, UHMW’s low friction helps reduce heat generation and enables operation with minimal lubrication. This helps avoid stick-slip and reduces overall system maintenance.
For applications where ultra-low friction is mandatory, engineers often compare UHMW tospring-energized PTFE seals — but UHMW often wins when abrasion resistance takes priority.
Beyond friction, UHMW’s chemical and moisture resistance broaden its usability across challenging media environments.
Chemical and moisture resistance
UHMW resists water, many solvents, dilute acids, and aggressive cleaning agents. Its exceptionally low moisture absorption makes it well-suited for humid or wet environments, including wastewater applications.
Virgin UHMW also meets food- and medical-grade requirements, aligning with Eclipse’s expertise inFDA- and medical-grade sealing.
Finally, UHMW is widely available and cost-effective, making it a practical option for high-volume and budget-conscious projects.
Cost-effectiveness and widespread availability
Compared to PTFE, PEEK, or UHMW alternatives, UHMW is significantly more economical. For high-volume OEM programs or cost-sensitive MRO schedules, UHMW provides outstanding value.
While these advantages are compelling, it’s equally important to understand UHMW’s limitations to avoid potential performance issues.
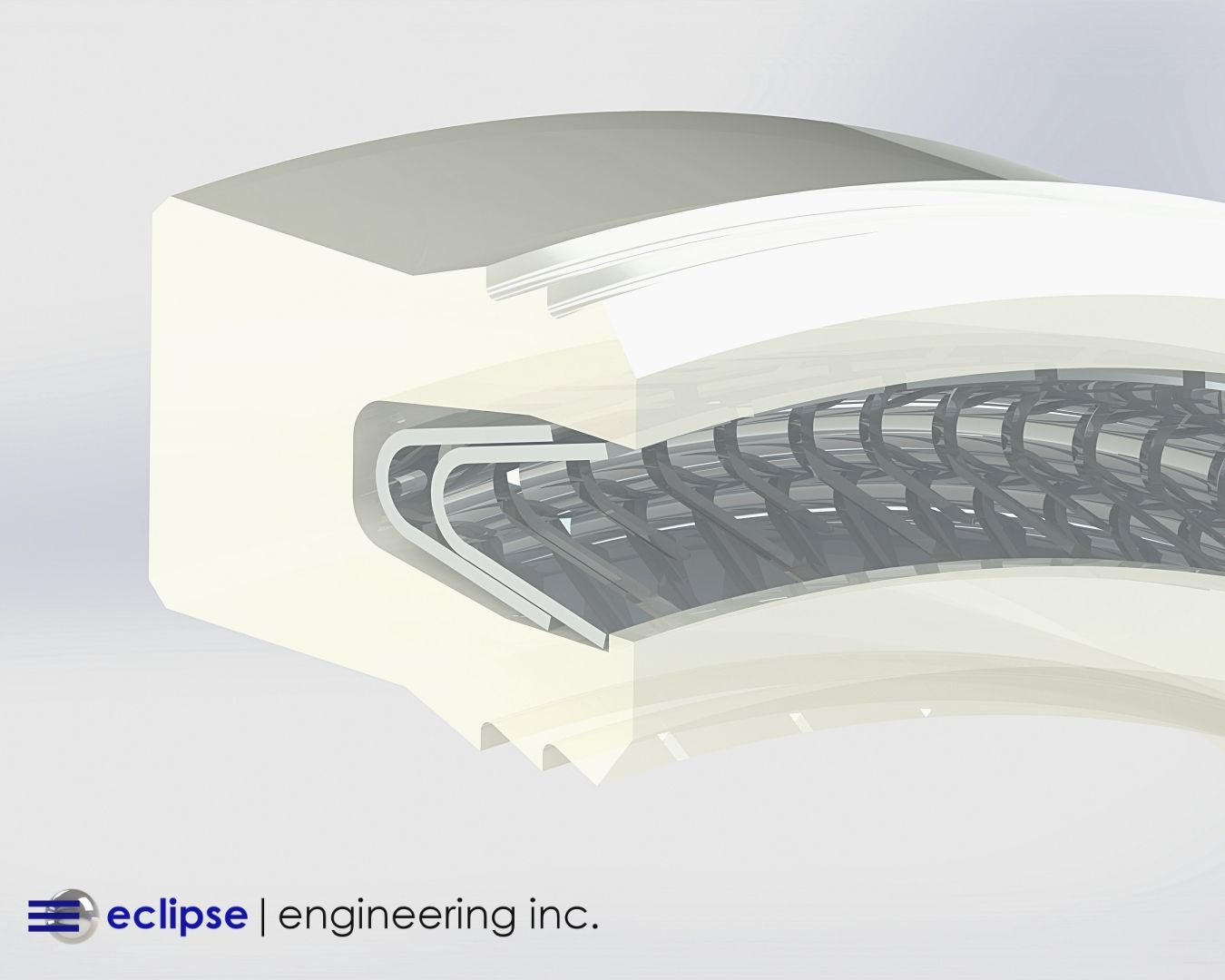
The Disadvantages of UHMW
Despite its strengths, UHMW is not the right material for every application. Engineers should weigh its limitations carefully during material selection.
Limited high-temperature performance
UHMW begins to lose strength around 150°F (65°C) and has a continuous operating limit near 180°F (82°C). For high-temperature or high-speed rotary applications, PTFE, PEEK, or engineered composites outperform UHMW.
This temperature sensitivity also restricts UHMW’s suitability for high-speed rotary sealing.
Not suitable for high-speed rotary sealing
Rotary motion generates frictional heat at the seal interface. Even at room temperature, this can push UHMW beyond its thermal limits and cause distortion, creep, or premature wear.
In these environments,spring-energized seals or PTFE rotary seals are generally recommended.
UHMW’s high coefficient of thermal expansion can further impact dimensional stability in precision applications.
High coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE)
UHMW exhibits significant dimensional changes with fluctuating temperatures. For tight-tolerance components, this can result in poor sealing performance or binding.
Additionally, machining and processing challenges make UHMW more difficult to fabricate for precision applications.
Machining and processing challenges
Because UHMW chips into long, continuous strands and is susceptible to heat distortion, precision machining requires expertise in polymer manufacturing. Eclipse frequently advises customers on best practices through its custom-engineered solutions.
Its lower stiffness also makes UHMW less suitable for heavy static loads.
Lower stiffness and deformation risk
Under heavy static load, UHMW can creep or deform. In applications requiring structural rigidity or long-term dimensional stability, harder polymers such as Nylon, acetal, or PEEK may be more appropriate.
Understanding these limitations sets the stage for knowing when UHMW is the right choice — and when alternative materials should be considered.
When UHMW Is the Right Choice — and When to Look Elsewhere
UHMW excels in applications involving:
- Abrasive or particulate-filled media
- Reciprocating motion (piston rods, cylinders)
- Scraper seals and wipers
- Low-lubrication or no-lubrication environments
- Food, beverage, and pharma conditions
- Cost-sensitive, high-volume parts
UHMW may not be suitable when:
- Temperatures exceed 150–180°F
- Rotary speeds produce high frictional heat
- Dimensional precision is critical
- Heavy static loads require higher stiffness
If UHMW does not meet the requirements, we may recommend PTFE, PEEK, or specialized engineered polymer composites.
Once the right application is identified, following best practices in design ensures UHMW performs optimally.
Best Practices for Designing with UHMW Seals
1. Account for thermal expansion in gland design
Because UHMW expands significantly with heat, glands must account for expansion, especially in dynamic applications.
Machining allowances also play a critical role in ensuring dimensional accuracy.
2. Allow for machining tolerances
Custom-machined UHMW components may require stress relief or dimensional allowances to ensure accuracy after processing. Eclipse’s custom machining services can assist with this step.
Material selection should also match motion requirements for optimal performance.
3. Use UHMW in reciprocating rather than rotary applications
Piston seals, wipers, guide rings, and wear surfaces are ideal candidates. Selecting the proper grade ensures chemical and compliance requirements are met.
4. Choose the correct UHMW grade
Options include:
- Virgin UHMW (FDA/food-grade)
- Reprocessed UHMW for cost-sensitive applications
- High-wear modified grades
Even with ideal design, planning for maintenance ensures longevity.
5. Plan for maintenance & wear monitoring
Even UHMW will wear down in abrasive applications. Designing components for easy replacement increases uptime and reduces unexpected failures.
Understanding these best practices sets the stage for real-world applications across industries.
Real-World Use Cases & Industries Where UHMW Seals Excel
UHMW is used widely across industries where abrasion resistance, moisture resistance, reliability, and cost-efficiency are top priorities.
- Paint, coating & slurry equipment: UHMW scraper seals, guide rings, and wipers dramatically outperform softer plastics.
- Resin, epoxy & adhesive dispensing: UHMW maintains wiping edges and prevents buildup.
- Food, beverage & pharmaceutical processing: Virgin UHMW is FDA-compliant and chemically inert.
- Manufacturing equipment wear components: Wear rings and guide bearings benefit from low friction and durability.
- Marine, coastal & wastewater environments: Low moisture absorption extends service life.
These use cases highlight how UHMW can deliver reliable, cost-effective performance when applied correctly.
Is UHMW Right for Your Application?
UHMW is not a universal material, but when specified correctly, it delivers excellent value in terms of longevity, abrasion resistance, friction performance, and total cost of ownership.
Eclipse Engineering’s experts help engineers and procurement teams evaluate whether UHMW — or an alternative like PTFE, PEEK, or engineered composites — is the best choice for your temperature, pressure, media, and motion requirements.
If you're evaluating UHMW for your next project, we’re here to help. Contact our engineering team, and we’ll review your specifications, recommend optimal materials, and engineer a solution built for long-term performance.